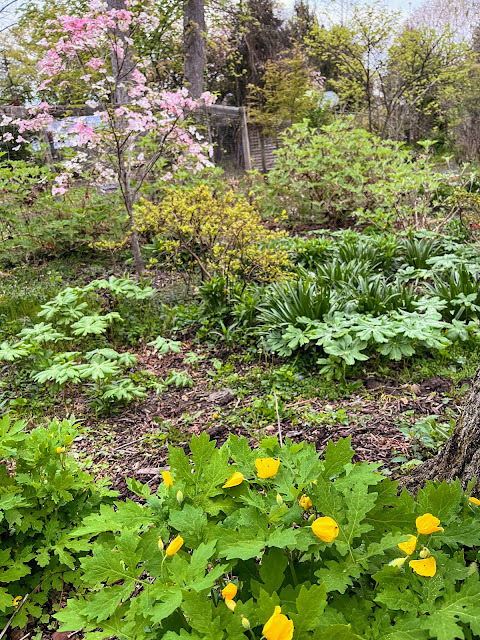
Ever heard of a painter whose spouse couldn't get him to paint the house? That's a bit like my backyard. While I've been doing plant work elsewhere this spring, my own backyard was quietly, stealthily taken over by an extraordinary array of spring weeds. The day of reckoning, or more likely several weeks of reckoning, has finally arrived.
First step, photograph them and write about them, on the chance that others might too find themselves wading through a backyard full of weeds and wonder what they all are. Click on a photo to make it larger.
This one, the most ridiculously successful, is purple deadnettle. It's in the mint family, which you can tell by its square stem, but unlike many other mints, it relies on seeds to spread, rather than underground rhizomes.
Here's more purple deadnettle, with a foreground of ground ivy. Ground ivy has other names: creeping Charlie, and gill over the ground. It spreads vegetatively above ground, across lawns, into garden beds. It could be charming if it weren't so aggressive. The same can be said for
mock strawberry.
Here's the ground ivy mixed in with some white clover at the bottom of the photo. The white clover hasn't been a problem, but in some situations, it too can become a sprawling mass.
Ground ivy looks like a wave here, rising out of the lawn and swamping the stonecrop Sedums. I really like the dandelions, until they go to seed, then not so much. If the soil is soft, gather all the basal leaves in your hand and give a slow, steady pull. Feed the leaves to your guinea pigs. Do people still have guinea pigs as pets?
By now, you'll recognize the ground ivy at the bottom of the photo, the purple dead nettle in the middle. Equally prevalent is hairy bittercress, which is the now brown plant in the upper left. A gardener feels a sense of defeat when, having delayed too long in pulling the hairy bittercress, its seeds come flying up at your face. It feels like mockery, the plant having successfully completed its life cycle and populated the ground with seeds for yet another year.
On the upper right in the photo are a few garlic mustards. They are edible, so I pull them, eat the seedheads, then toss the plant where it won't reroot. My yard would be full of them, too, if they were as stealthy and quick to generate seeds as the bittercress. Being larger than bittercress, garlic mustard is more satisfying to pull, and since it is slower to mature its seeds, we can go through a period of procrastination and still pull it in time. Garlic mustard is a biennial, meaning it grows some basal leaves the first year, building up energy in the root, then launches a flowering stalk the next spring. If not pulled, it will go to seed, then turn yellow and die in mid-summer, its work done.
That's a different approach from many of these spring weeds--hairy bittercress, purple deadnettle, common chickweed, henbit, etc.--which
sprout from their seeds in the fall, overwinter in the vegetative state, then get a quick start in the spring, blooming and setting seed before distracted people like me can pull them.
At the top of this photo is hairy bittercress before it turns brown. On the left is Canada thistle, which has taken over many a garden bed in Princeton, spreading underground, popping up all over. I keep it at bay but have not been organized or persistent enough to fully get rid of it.
At the bottom there are violet leaves.
I'd like to say that the violets are less aggressive. They integrate into the lawn rather than taking it over, sprinkling attractive blooms hither and yon, and the leaves and flowers are good in salads, or steamed. But even they started being way too pushy in the flower beds a couple years ago, prompting a major weeding out. If salad makings weren't so easy to get in the local store, we'd be eating violet leaves, feeling just fine and with more balanced gardens to show for it.
Happy to say that I have no lesser celandine in my yard--the most problematic of the spring weeds, given its capacity to take over and then spread into the neighbor's yard and nature preserves. There was one in the yard a few years ago, but one medicinal spritz of herbicide was all it took to nip it in the bud. The leaves are reminiscent of violets, but are less curled, lighter green, and more leathery in appearance.
Mugwort, down there at the bottom, is a tough customer that has taken over many gardens, raingardens, and fields. Recurrent pulling has limited it to one place in my garden, but it spreads to form monocultures along the gas pipeline right of way along the Princeton ridge. Above and left in the photo is a kind of horsetail that has inculcated itself into one of the flower beds, probably planted decades ago by a previous owner.
I remember Veronica (speedwell) from my field botany days. It has an interesting bi-colored flower, and in our Michigan yard it had seemed harmless enough. When it showed up in our Princeton yard a few years ago, I let it grow here, but, perhaps due to a sunnier yard and abundant rains,
it exploded this year and became, like so many problems in the world, too much of a good thing.
Chickweed hasn't been much of a problem.
Curly dock is easy to undercut with a shovel.
You see that little triplet of leaflets sticking out at the bottom? That's wild strawberry. I thought it would be great to have wild strawberries in the garden--native, tasty little berry. But they spread like crazy and I happened upon only one berry over the years.
Another weed that's here and there and can easily be pulled from wet ground is rough avens. To its left in the photo is a native weed called willow herb. Both of these look like they might generate attractive flowers, but don't quite generate enough show to be considered ornamental.
Wood sorrel, bottom of the photo, is a common greenhouse weed, but not much of an issue in a garden. Its leaves look somewhat like clover, but are tangy with the taste of oxalic acid.
The green leaves towards the top of the photo are jewelweed, a native annual that can be rambunctious, but which I appreciate for its tubular orange flowers that attract hummingbirds.
Most of these weeds originally hitchhiked to America from other continents. Finding early on as a gardener that most of my labors involved saving the intended plants from these overly enthusiastic weeds set the groundwork for understanding the problem of invasive species in nature preserves.
The reader may by now have concluded that my garden is largely a battleground where a distracted gardener is little match for weeds that grow 24/7. But there are areas where balance is easier to maintain, where celandine poppies, redbuds and dogwoods start a pleasing progression of flowers that continues through the spring.